GB-39 - Suspended Bell
悬钟 - Xuán zhōng
Point Region: Leg
GB-39, or 'Xuanzhong' (meaning 'Suspended Bell'), is a key point in the entire acupressure system. Located on the side of the lower leg, its name refers to its ability to address issues related to the 'bell' or 'bell-like' sound of the ankle, as well as a sense of 'swelling' or 'fullness' in the lower leg.
As a local point, Xuanzhong is primarily used for issues related to the ankle and leg, such as a stiff ankle, a sore ankle, and a sense of 'weakness' in the lower body. It is a go-to point for 'tonifying' the Kidney and 'strengthening' the body as a whole. By stimulating this point, you can help to restore a sense of balance and harmony to the entire body.
Xuanzhong acts as a vital access point to the core of the body, providing a direct and effective way to address blockages and restore a sense of comfort and vitality to the lower body.
Location & How to Find
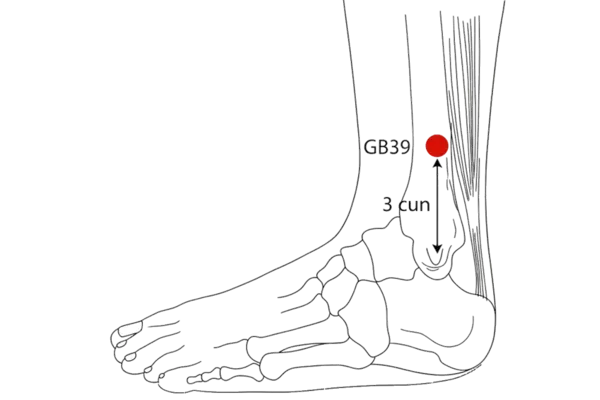
Anatomical Location: On the lateral lower leg, anterior to the fibula, above the lateral malleolus.
How to Locate:
- Locate your outer ankle bone (lateral malleolus)
- Move up about 3 finger widths from the ankle bone
- Feel along the front edge of the fibula
- Find the depression above the ankle
- This is GB-39, the influential point for marrow
Primary Functions
Musculoskeletal System
- Strengthens bones and prevents osteoporosis
- Treats bone marrow disorders
- Relieves ankle and lower leg pain
- Improves bone density and health
Nervous System
- Treats neck stiffness and cervical disorders
- Relieves nerve compression
Liver & Gallbladder System
- Nourishes liver and kidney essence
- Supports bone and marrow health
- Harmonizes gallbladder function
Immune & Energy System
- Strengthens constitutional energy
- Boosts marrow and blood production
Clinical Applications
Primary Indications
- Neck pain
- Bone disorders
- Marrow deficiency
- Osteoporosis
- Joint stiffness
- Weak bones
- Spinal problems
- Developmental delays
Related Health Concerns
Common Conditions:
Related Acupoints
Select a point to learn about its location, primary functions, clinical applications, and protocols.
GB-39 Protocols
N/A