GV-19 - Behind the Crown
后顶 - Hòu dǐng
Point Region: Head (back)
GV-19, or 'Hou Ding' (meaning 'Posterior Summit'), is a local point located on the back of the head. Its name refers to its position as a 'summit' or 'peak' on the back of the head, where it can address issues related to the mind and the nervous system.
As a local point, Hou Ding is primarily used for issues related to the head and neck, such as a headache, dizziness, and a sense of 'stuckness' in the head. It is a go-to point for 'calming' the mind and 'clearing' emotional blockages in the head. By stimulating this point, you can help to restore a sense of peace and tranquility to the mind and body.
Hou Ding acts as a vital access point to the core of the body, providing a direct and effective way to address blockages and restore a sense of comfort and vitality to the upper body. It's a reminder of the power of local points to provide targeted relief and restore a sense of comfort and vitality to the entire body.
Location & How to Find
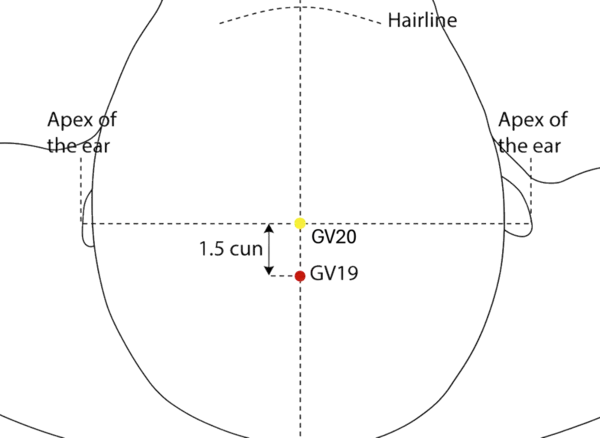
Anatomical Location: On the posterior midline of the scalp, 1.5 cun superior to GV-18.
How to Locate:
- Locate GV-18 on the back of your head
- Move up 1.5 finger widths toward the crown
- You're now approaching the back portion of the top of your head
- Feel for the point on the skull surface
- This is GV-19
Primary Functions
Nervous System
- Enhances brain function and intelligence
- Improves memory and cognitive abilities
- Calms the mind and reduces mental agitation
Emotional & Mental
- Reduces anxiety and emotional stress
- Improves mental clarity and focus
- Enhances emotional stability
Musculoskeletal System
- Relieves vertex headaches
- Strengthens crown and head region
- Improves cranial circulation
Circulatory System
- Improves blood circulation to brain
- Enhances cerebral blood flow
Clinical Applications
Primary Indications
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Insomnia
- Epilepsy
- Mental disorders
- Blurred vision
- Vertex headache
- Amnesia
Related Health Concerns
Common Conditions:
Related Acupoints
Select a point to learn about its location, primary functions, clinical applications, and protocols.
GV-19 Protocols
N/A